ICE Scoring Model: How to Prioritize Fast


Prioritizing with the ICE model is one of the fastest ways to rank your backlog. The ICE scoring model uses just three factors (Impact, Confidence, and Ease) instead of RICE's four. It's popular with growth teams who need to prioritize experiments quickly.
This guide covers how ICE works, when to use it over RICE, and includes a free template.
The ICE model is a framework that prioritizes ideas or projects based on their Impact, Confidence, and Ease. In product management, the ICE framework has become a standard tool for making data-driven decisions.
Sean Ellis, famous for coining the term "growth hacking", invented this prioritization model. ICE originated in the growth hacking community, where rapid experimentation requires quick prioritization decisions.
The ICE framework helps you make a "good enough" guess at priority. It's not perfect, but it helps you figure out which features are awesome and which ones you should probably skip.
ICE stands for three factors (the three ICE criteria):
The ICE score formula:
ICE Score = Impact x Confidence x Ease
It's like the classic impact/effort analysis, but with confidence thrown in for good measure. The ICE scoring method gives you a repeatable system for decision making.
Let's break down each component and then we'll walk through the process of using ICE for prioritization. Once you understand these ICE criteria, you can build an ICE matrix to compare all your features side by side.
Impact measures how much a feature contributes to your goals. Before scoring impact, ensure your goals are clearly defined. A great tool for this is the Product Vision Board, which helps you articulate your vision, target group, needs, product, and business goals.
When scoring impact, use a 1-10 scale. Here's an example scale:
| Impact Description | Score |
|---|---|
| Transformative: Game-changing for the product | 10 |
| Very High: Significant improvement for many users | 8-9 |
| High: Notable improvement for some users | 6-7 |
| Medium: Moderate improvement for a few users | 4-5 |
| Low: Minor improvement for a small number of users | 2-3 |
| Very Low: Barely noticeable improvement | 1 |
Examples
Confidence helps distinguish between data-backed ideas and mere opinions. It's crucial to involve your team when determining confidence scores, as different perspectives can reveal potential concerns.
Here's a scale you can use for Confidence:
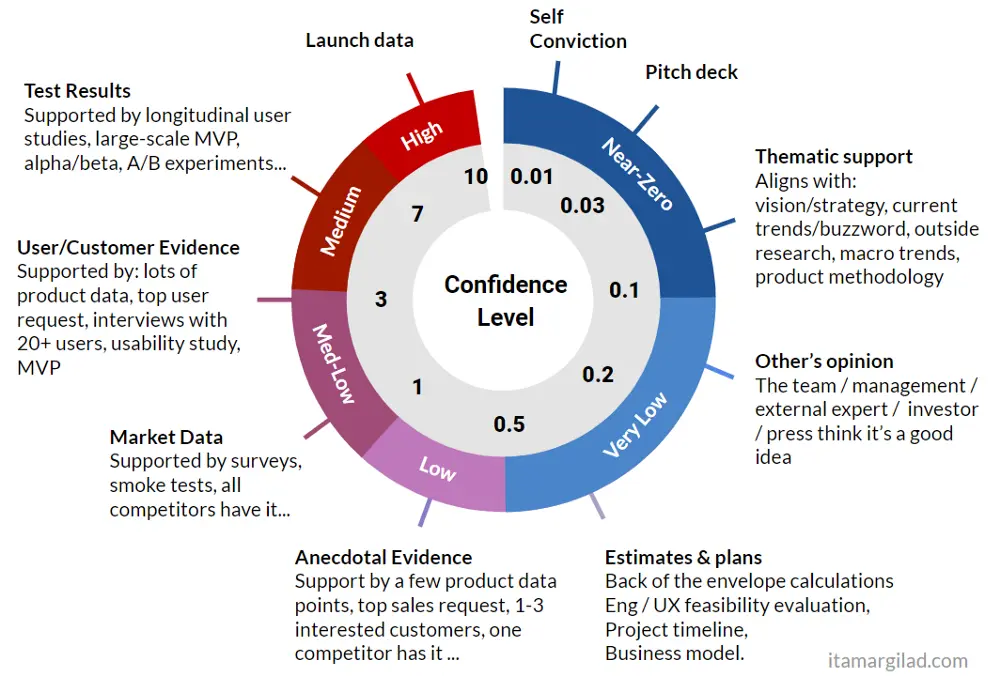
(Source: Itamar Gilad)
Example
Ease is all about how hard it is to implement something. Think of this as the traditional effort factor. How long will it take to build?
Here's an example scale for Ease:
| Person weeks | Ease |
|---|---|
| < 1 week | 10 |
| 1-2 weeks | 9 |
| 2-3 weeks | 8 |
| 4-5 weeks | 7 |
| 6-7 weeks | 6 |
| 8-9 weeks | 5 |
| 10-12 weeks | 4 |
| 13-16 weeks | 3 |
| 17-25 weeks | 2 |
| > 26 weeks | 1 |
(Source: Itamar Gilad)
Examples
Now that we understand the components, let's walk through the process of using ICE for prioritization.
First things first, make a list of all the tasks and features you're thinking about.
Try to keep things MECE (Mutually Exclusive, Collectively Exhaustive). This means your items should not overlap (mutually exclusive) and should cover all possibilities (collectively exhaustive).
For example, "SSO login" and "Tagging" are on the same level and don't overlap. But "Change button color" and "Build a whole new app" are definitely not on the same level.
Take your time to make a good list. It's a pain when you're halfway through prioritizing and someone throws in a new idea. I usually ask customers, partners, and coworkers for their input using surveys or a feedback tool.
Let's add the list in the Score-based Prioritization module:
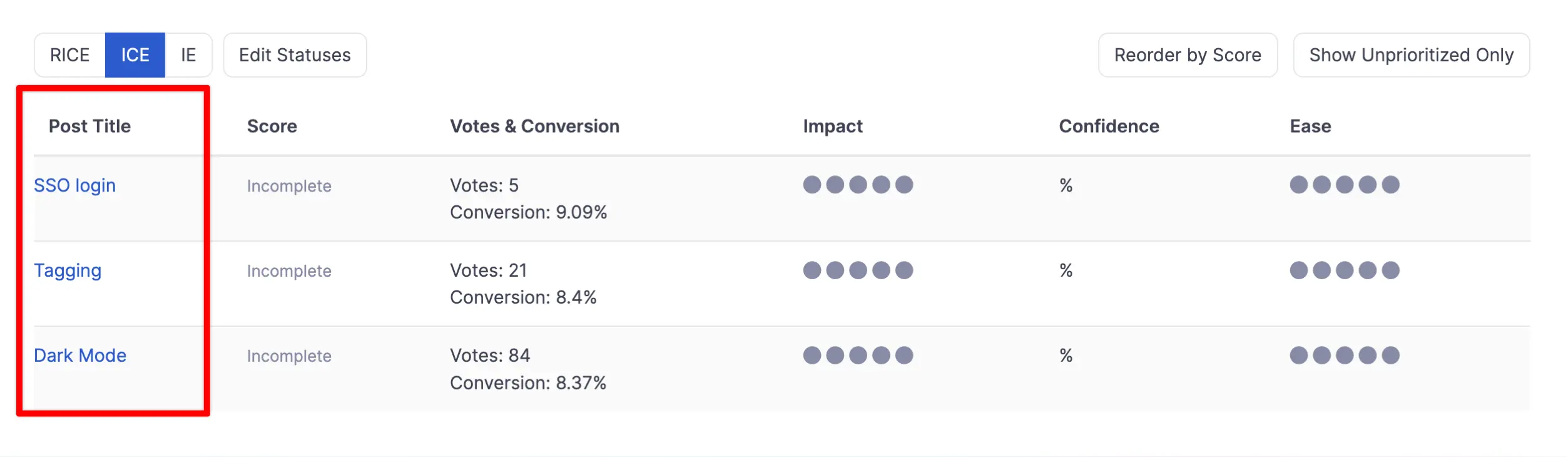
Now, go through your list and score each item on Impact, Confidence, and Ease using the scales we discussed earlier.
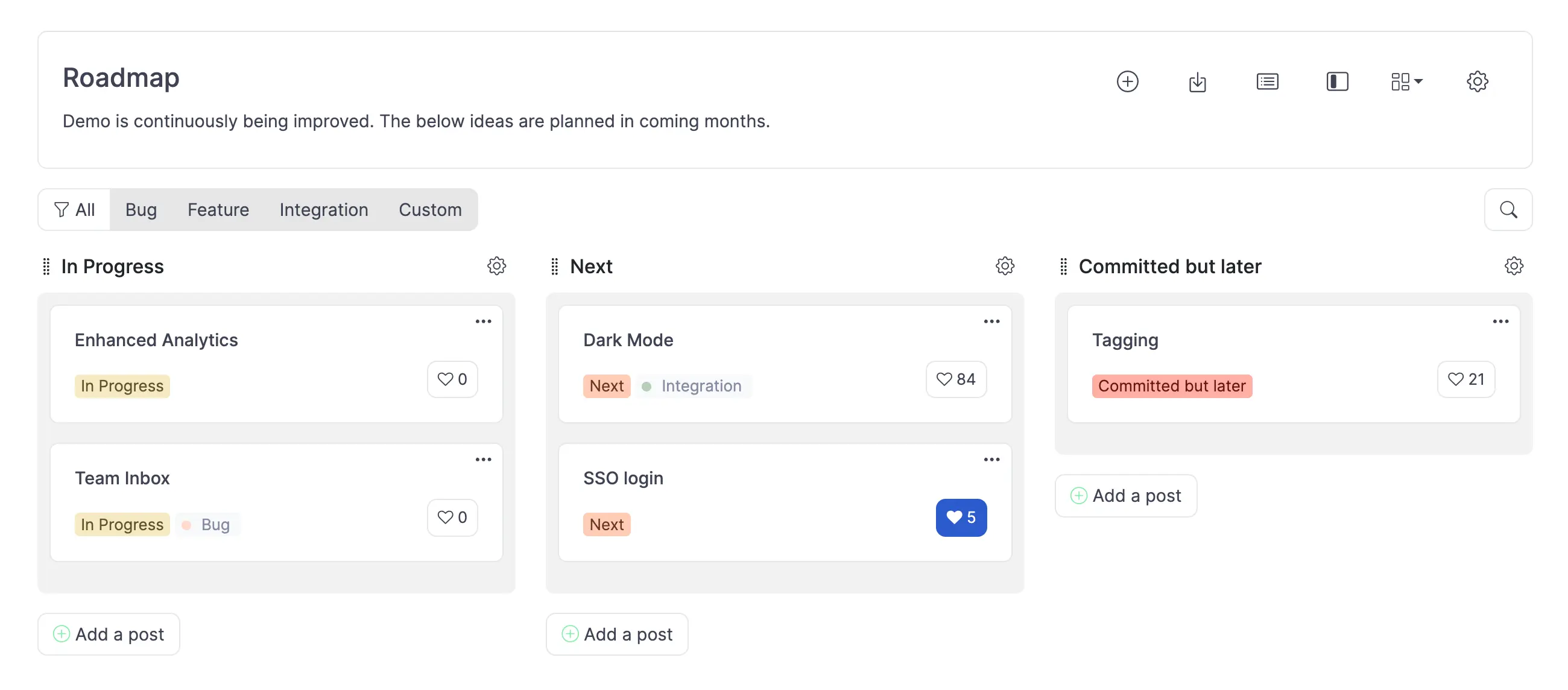
In our ICE prioritization tool, we make decisions based on how many votes a feature gets. We also look at conversion, which is likes divided by views. Even though the SSO login feature has fewer votes, it has the highest conversion rate, showing it's important.
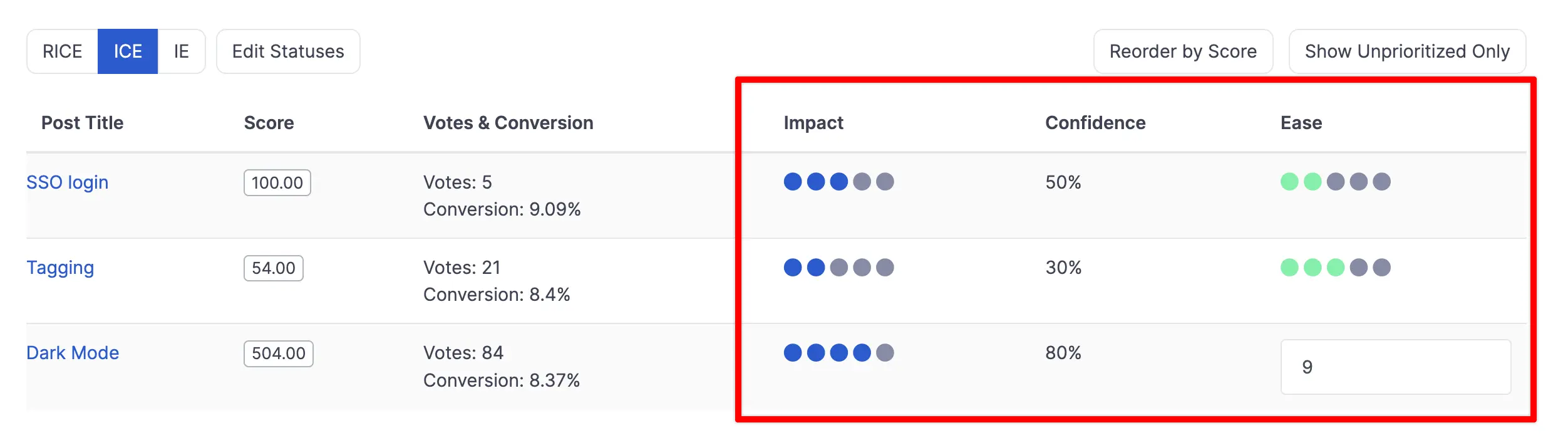
Now it's time to do some math! The ICE score calculation is simple:
Priority = Impact x Confidence x Ease
After entering all the data, the tool automatically calculates the ICE score. You can also use this online ICE score calulator.
With the ICE scores calculated, we can reorder the list to create an ICE ranking from highest to lowest priority. This ICE priority list helps in identifying which features should be addressed first.
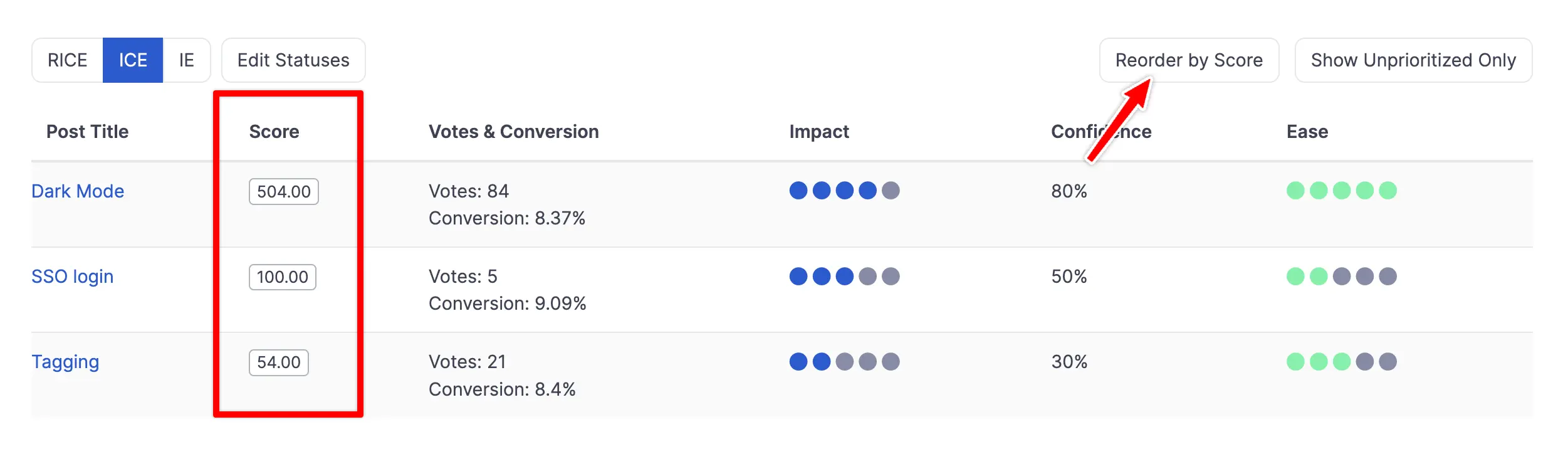
After calculating the scores, it's important to review the results with your team and key stakeholders. This step helps catch any oversights and ensures everyone is aligned on the priorities.
Finally, with all the data entered, we can use this input to determine the roadmap.
We review each item on the list. In ProductLift, we can change the status of the items we have reviewed. This step immediatly updates users that votes for the feature request.
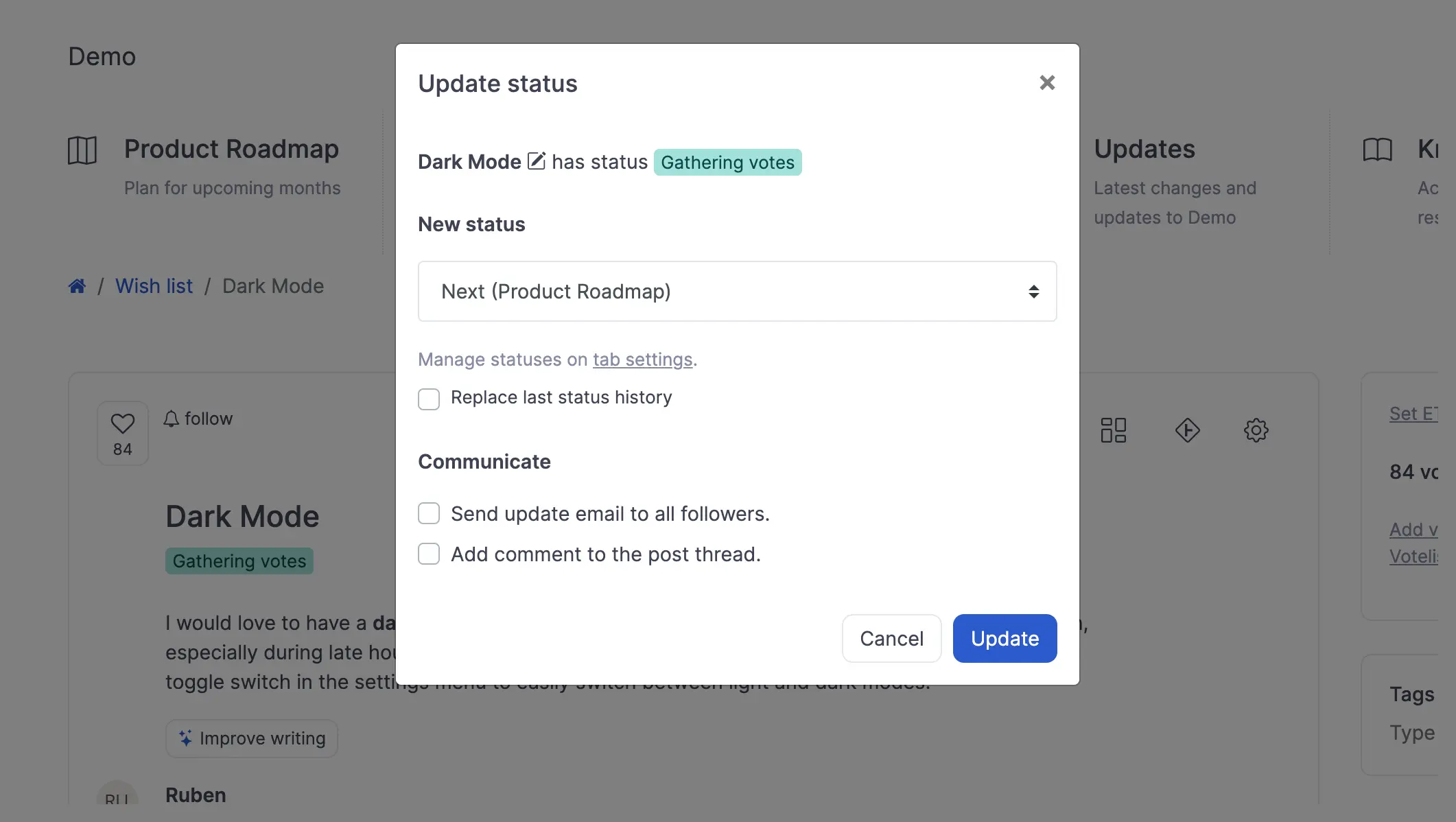
As we update the statuses of the items, they are automatically added to our roadmap. This ensures that our roadmap is always up-to-date with the latest priorities and statuses.
Many successful companies have used ICE to drive their product development. Here are a couple of examples:

Airbnb used the ICE product management to choose which features to build that would make people trust their platform more and book more easily. By focusing on the ideas that scored highest, they made their website easier to use and got more hosts and guests to join.

Dropbox used ICE to figure out which features would make people use their app more often and stick around longer. By building the high-scoring features first, Dropbox grew really fast and became super successful.
While the ICE framework is a powerful tool, it can be time-consuming to implement manually, especially for a large number of features. This is where AI-powered prioritization can come in handy.
The AI prioritization feature helps us decide which features to focus on in 30 seconds.
We start by setting up our product vision and adding features we want to consider. As users vote on their favorites, the AI analyzes this data and our vision to find the top 5 features.

RICE is another popular prioritization framework that stands for Reach, Impact, Confidence, and Effort. The main difference is the addition of the Reach factor, which considers how many people the feature will affect in a given time period.
So which is better? It depends on your needs:
In general, if you're just starting out or need to make quick decisions, ICE is a great choice. As your product matures and you have more data about your users, you might want to consider switching to RICE prioritization for more nuanced prioritization. You can try both with our free RICE calculator.
For a detailed comparison of both frameworks, see our RICE vs ICE guide.
The ICE prioritisation framework can be a powerful tool for product managers, but it's important to use it properly. Here are some do's and don'ts to keep in mind when applying ICE:
Do:
Start by clearly defining your objectives and goals
Involve the right stakeholders in the prioritization process
Use the ICE score to prioritize features or ideas, but also consider other factors such as resources, technical feasibility, and market demand
Revisit and update your ICE priority regularly as new information becomes available or priorities change
Communicate your prioritization decisions transparently and explain the rationale behind them
Use an ICE template and agree on scales across the team(s)
Don't:
Rely solely on the ICE methodology to make decisions. Use it as one of several inputs in your prioritization process
Ignore feedback from users or other stakeholders just because a feature or idea scored low on the ICE scale
Rush through the prioritization process without giving it enough time and attention
Base your ICE scores solely on your own opinions or assumptions. Use data and insights from multiple sources to inform your scores
Use ICE as a one-size-fits-all solution. Different projects or products may require different prioritization frameworks or approaches
Frequently Asked Questions
ICE stands for Impact, Confidence, and Ease. These three criteria form the basis of the ICE scoring framework, helping teams evaluate and prioritize features or initiatives objectively.
An ICE score is a numerical value that represents the combined Impact, Confidence, and Ease of a feature or initiative. When using a 1-10 scale for each factor, the ICE score ranges from 1 to 1000. Higher scores indicate features that should be prioritized first.
The ICE method is a prioritization technique where you score each idea on three factors (Impact, Confidence, Ease), multiply them together, and use the resulting score to rank your priorities. It's a quick and effective way to make objective prioritization decisions.
To calculate an ICE score, assign a value (typically 1-10) to each of the three factors: Impact, Confidence, and Ease. Then multiply them together: ICE Score = Impact × Confidence × Ease. For example, a feature with Impact 8, Confidence 7, and Ease 6 would have an ICE score of 336.
The ICE model of prioritization is a framework used to evaluate and prioritize ideas or projects based on three factors: Impact, Confidence, and Ease. It helps teams focus on initiatives that will yield the most significant results with the least effort and highest confidence in success.
The ICE formula is calculated by multiplying the scores of Impact, Confidence, and Ease. The formula is:
ICE score = Impact x Confidence x Ease
Each factor is typically scored on a scale from 1 to 10, with higher scores indicating higher potential for success.
To perform ICE prioritization, start by listing all potential ideas or projects. For each, assign a score for Impact (how much it will positively affect the goal), Confidence (how certain you are that it will succeed), and Ease (how easy it is to implement). Multiply the three scores to get the ICE score. Rank your projects based on these scores, with higher-scoring projects taking priority.
The ICE approach is a simple yet effective method for prioritizing projects or initiatives by focusing on those that offer the best combination of high impact, confidence in success, and ease of execution. It helps streamline decision-making and focus resources on the most promising opportunities.
Prioritizing features is tough and takes time and discipline. The ICE prioritization framework helps you make a "good enough" estimate of priority. Now you have the tools to do this for your product.
Remember to revisit your ICE scores regularly, as your experience, goals, and confidence will change over time.
Finally, share your priority outcomes with your customers and stakeholders using your product roadmap or kanban board. This keeps everyone aligned and excited about what's coming next!
If you're ready to move beyond spreadsheets, try ICE prioritization in ProductLift. It automatically calculates scores, integrates with user feedback, and generates your roadmap.
More ICE Resources:
Related Frameworks:
Join over 3,051 product managers and see how easy it is to build products people love.
Did you know 80% of software features are rarely or never used? That's a lot of wasted effort.
SaaS software companies spend billions on unused features. In 2025, it was $29.5 billion.
We saw this problem and decided to do something about it. Product teams needed a better way to decide what to build.
That's why we created ProductLift - to put all feedback in one place, helping teams easily see what features matter most.
In the last five years, we've helped over 3,051 product teams (like yours) double feature adoption and halve the costs. I'd love for you to give it a try.

Founder & Digital Consultant
See how real product teams use RICE, ICE, MoSCoW, and other prioritization frameworks. 6 practical examples with actual scores, decisions, and outcomes.
A practical decision guide for choosing the right product prioritization framework. Answer 4 questions to find the best framework for your team size, data, and decision type.
Side-by-side comparison of 10 product prioritization frameworks. Compare RICE, ICE, MoSCoW, Kano, and others on scoring type, complexity, data needs, and best use cases.
The best prioritization frameworks for startups at every stage. From pre-PMF to growth, learn which framework fits your team size, data, and speed requirements.
Learn when to promote feature requests to your roadmap, how to merge duplicates, notify voters, and keep credibility through the full lifecycle.